Introduction: The Frosty Path to Metabolic Mastery
Cold thermogenesis—deliberate exposure to cold temperatures—has surged in popularity as a biohacking strategy to boost metabolism, enhance resilience, and optimize health. From ice baths to cryotherapy, this practice leverages the body’s primal response to cold to ignite calorie-burning mechanisms. But how exactly does chilling your body rev up your metabolic engine? This article dives into the science, benefits, and practical applications of cold thermogenesis, unpacking its role in unlocking a faster, more efficient metabolism.
The Science of Cold Thermogenesis: How Shivering Ignites Fat Burn
When exposed to cold, the body activates survival mechanisms to maintain core temperature. Brown adipose tissue (BAT), a specialized fat packed with mitochondria, becomes metabolically active, converting stored energy into heat—a process called non-shivering thermogenesis. Meanwhile, shivering generates heat through rapid muscle contractions. Studies show that cold exposure can increase calorie expenditure by up to 30%, with BAT activation playing a starring role. Researchers at the National Institutes of Health found that regular cold exposure enhances BAT density, effectively turning the body into a furnace for burning white fat stores.
Metabolic Rate 101: Understanding Your Body’s Energy Engine
Your basal metabolic rate (BMR)—the calories burned at rest—dictates energy efficiency. Factors like age, muscle mass, and genetics influence BMR, but cold thermogenesis offers a lever to amplify it. By stimulating BAT and upregulating thermogenic proteins like UCP1, cold exposure forces the body to work harder, creating a sustained metabolic boost. Unlike fleeting diet-driven spikes, this adaptation fosters long-term efficiency, akin to upgrading a car’s engine to burn fuel more effectively.
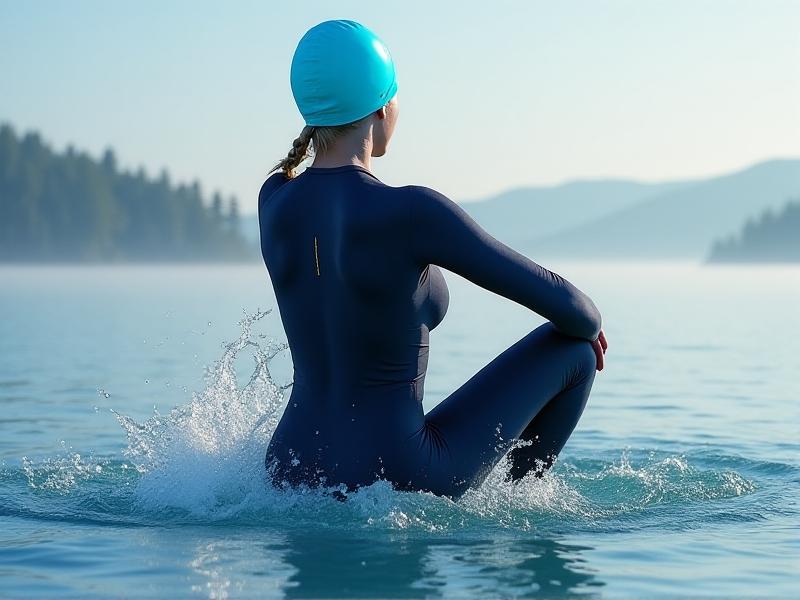
Cold Exposure Protocols: From Mild to Wild
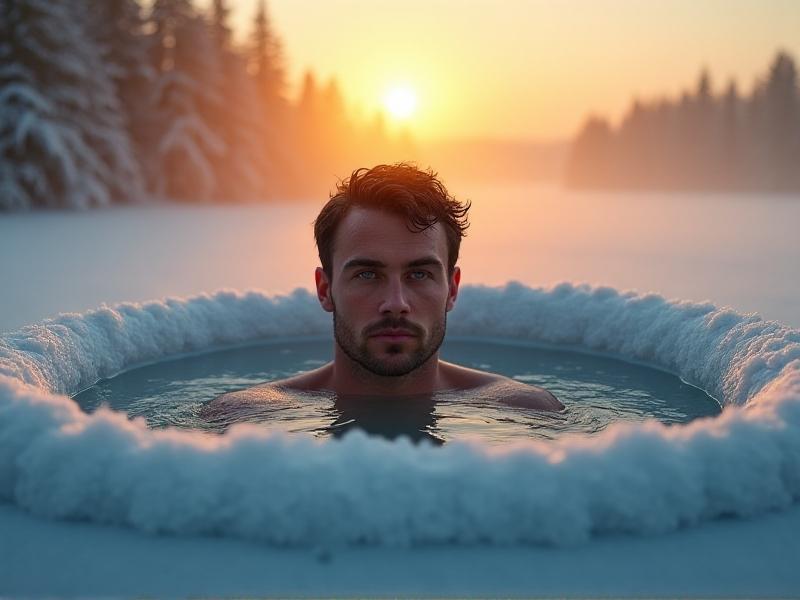
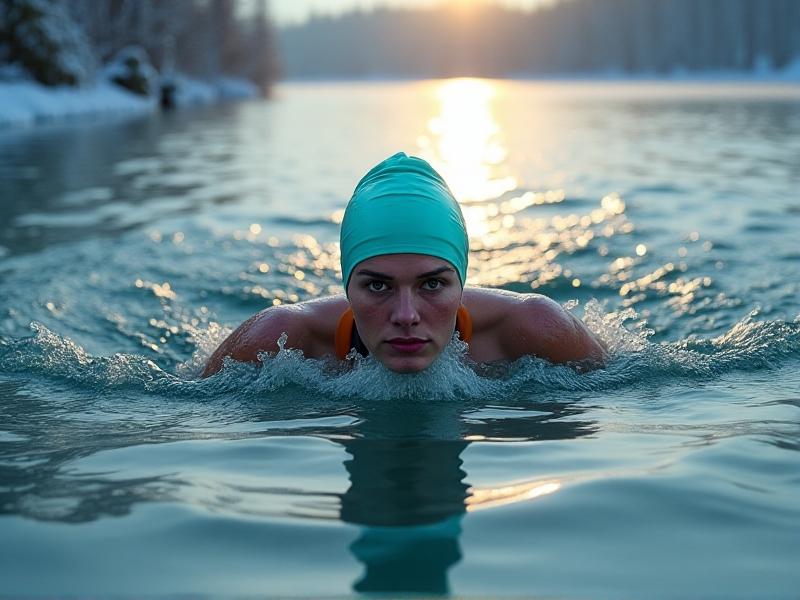
Incorporating cold thermogenesis doesn’t require polar plunges. Beginners might start with 30-second cold showers, gradually increasing duration as tolerance builds. Advanced practitioners often use ice baths (10–15°C for 5–10 minutes) or outdoor swims. A 2022 study in theJournal of Thermal Biology
noted that 11 minutes of weekly cold exposure spread across 2–3 sessions significantly elevated metabolic markers. Consistency trumps intensity: regular, manageable exposure primes the body’s adaptive response without overwhelming it.

The Hormonal Symphony: How Cold Sparks Adrenaline and Irisin
Cold triggers a hormonal cascade: adrenaline and noradrenaline surge, sharpening focus and mobilizing fat. Meanwhile, the hormone irisin, released during shivering, converts white fat into BAT. A 2019 Harvard study linked irisin to improved insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial biogenesis—key for metabolic health. However, chronic overexposure can spike cortisol. Balancing frequency and recovery ensures hormones work in harmony, not chaos.Cold Thermogenesis Myths: Separating Fact from Frostbite Fiction
Myths abound, like “the colder the better” or “cold alone melts fat.” In reality, extreme cold risks hypothermia, and fat loss requires sustained calorie deficits. Cold thermogenesis is a tool, not a magic bullet. It complements nutrition and exercise by optimizing metabolic efficiency. Another misconception: BAT activation negates the need for muscle. In truth, muscle mass remains critical—BAT and muscle synergize to maximize energy expenditure.Safety First: Avoiding the Ice-Cold Pitfalls
Cold exposure demands respect. Never immerse alone, and avoid prolonged sessions. Numbness, dizziness, or blue lips signal overexposure. Cardiac patients should consult doctors, as cold shocks can strain the heart. Gradual acclimatization—lowering water temperature incrementally—reduces risks. Pairing cold therapy with breathwork (e.g., Wim Hof Method) enhances tolerance and control.Beyond Metabolism: Cold’s Cognitive and Immune Perks
Cold thermogenesis isn’t just metabolic. Studies link it to reduced inflammation, sharper cognition, and enhanced immune response. The norepinephrine released during cold exposure improves mood and focus, while cold showers correlate with fewer sick days. These ancillary benefits make it a holistic upgrade, not just a weight-loss tactic.Integrating Cold Thermogenesis Into Daily Life
Start small: end showers with 30 seconds of cold, or walk outdoors in minimal layers. Track progress via metabolic wearables like Oura Ring or Whoop. Pair with protein-rich meals to support muscle retention. Timing matters—morning exposure energizes, while evening sessions may disrupt sleep. Customize protocols to align with lifestyle and goals.The Future of Cold Therapy: Research and Innovations
Emerging tech like localized cooling devices and cryolipolysis refine cold’s metabolic potential. Researchers explore “cold mimetics”—drugs that activate BAT without actual exposure. Meanwhile, wearable tech democratizes metabolic monitoring. As science unravels cold’s full impact, one truth endures: harnessing this primal stressor taps into an evolutionary blueprint for vitality.Advertisement
Recommended Reading: Lymphatic System Stimulation via Cold Showers
























Comments
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *