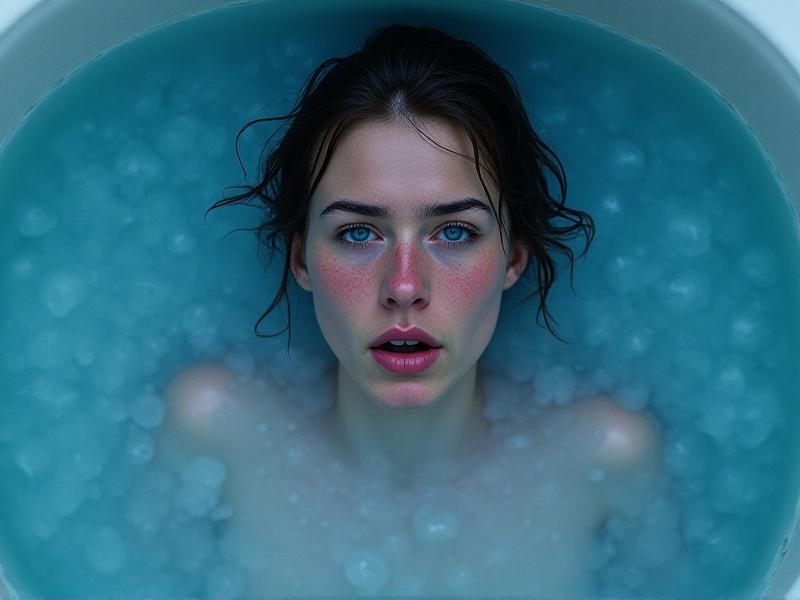
Understanding the Cold Shock Response: A Biological Survival Mechanism
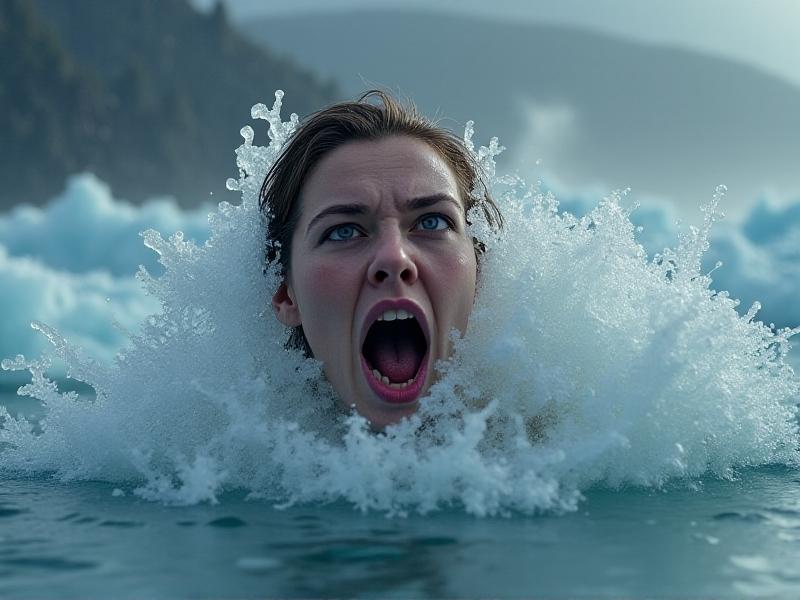 The human body's reaction to sudden cold water immersion is both immediate and violent. Within seconds, a cascade of physiological responses—rapid breathing, gasping, and a surge in heart rate—threatens to override rational thought. This cold shock response, while evolutionarily designed to prioritize survival, becomes a leading cause of drowning deaths in cold water environments. Researchers have clocked the onset of these symptoms occurring within 30 seconds of exposure to water temperatures below 15°C (59°F), with full-body immersion amplifying the effects through rapid conductive heat loss.
The human body's reaction to sudden cold water immersion is both immediate and violent. Within seconds, a cascade of physiological responses—rapid breathing, gasping, and a surge in heart rate—threatens to override rational thought. This cold shock response, while evolutionarily designed to prioritize survival, becomes a leading cause of drowning deaths in cold water environments. Researchers have clocked the onset of these symptoms occurring within 30 seconds of exposure to water temperatures below 15°C (59°F), with full-body immersion amplifying the effects through rapid conductive heat loss.
Why Mitigation Matters: The Hidden Dangers of Cold Water Immersion
 Each year, maritime authorities report hundreds of preventable deaths linked to inadequate cold water preparation. The critical first three minutes of immersion prove most lethal, as uncontrolled hyperventilation leads to water aspiration. Beyond initial survival, secondary threats like hypothermia onset (within 30 minutes) and limb paralysis create compounding risks. Vulnerable populations including children, seniors, and individuals with cardiovascular conditions face exponentially higher mortality rates even in relatively mild cold water exposures.
Each year, maritime authorities report hundreds of preventable deaths linked to inadequate cold water preparation. The critical first three minutes of immersion prove most lethal, as uncontrolled hyperventilation leads to water aspiration. Beyond initial survival, secondary threats like hypothermia onset (within 30 minutes) and limb paralysis create compounding risks. Vulnerable populations including children, seniors, and individuals with cardiovascular conditions face exponentially higher mortality rates even in relatively mild cold water exposures.
Physiological Preparation: Training the Body's Cold Resistance
 Controlled cold exposure therapy has emerged as a vital training protocol for maritime professionals and outdoor enthusiasts. Regular 2-3 minute cold showers or supervised ice bath sessions can significantly dampen the gasp reflex. The Wim Hof Method, combining breathing exercises with gradual cold exposure, has shown particular promise in peer-reviewed studies. Navy survival training programs now incorporate progressive cold water drills, improving participants' thermal tolerance by 40-60% over eight-week periods.
Controlled cold exposure therapy has emerged as a vital training protocol for maritime professionals and outdoor enthusiasts. Regular 2-3 minute cold showers or supervised ice bath sessions can significantly dampen the gasp reflex. The Wim Hof Method, combining breathing exercises with gradual cold exposure, has shown particular promise in peer-reviewed studies. Navy survival training programs now incorporate progressive cold water drills, improving participants' thermal tolerance by 40-60% over eight-week periods.
Environmental Mastery: Navigating Cold Water Conditions
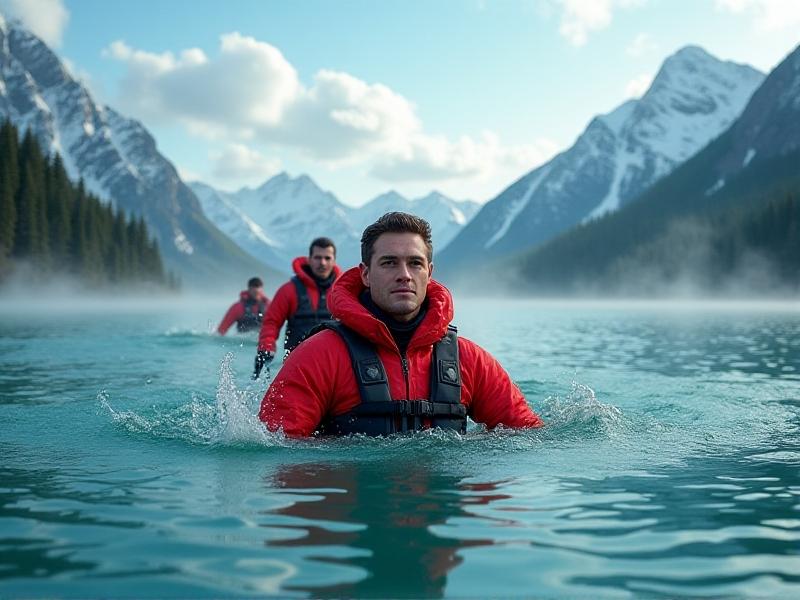 Water temperature awareness forms the cornerstone of cold water safety. The "1-10-1 Principle"—1 minute to control breathing, 10 minutes of functional movement, 1 hour before unconsciousness—guides survival planning. Modern marine weather apps now provide real-time coastal water temperatures alongside wave height predictions. Coastal rescue teams emphasize the 'Float First' protocol for unexpected immersion victims, delaying swimming attempts until breathing stabilizes.
Water temperature awareness forms the cornerstone of cold water safety. The "1-10-1 Principle"—1 minute to control breathing, 10 minutes of functional movement, 1 hour before unconsciousness—guides survival planning. Modern marine weather apps now provide real-time coastal water temperatures alongside wave height predictions. Coastal rescue teams emphasize the 'Float First' protocol for unexpected immersion victims, delaying swimming attempts until breathing stabilizes.
Behavioral Countermeasures: From Panic to Purposeful Action
Controlled breathing techniques prove most effective when practiced to muscle memory. The Navy SEAL-derived box breathing method (4-second inhale, 4-second hold, 4-second exhale) breaks the hyperventilation cycle. Survival instructors teach the "Hum Technique"—prolonged exhale humming—to maintain airway pressure and prevent water inhalation. These methods have shown 73% effectiveness in preventing aspiration during controlled cold water trials.Technological Armor: Innovations in Thermal Protection
Material science breakthroughs are redefining cold water safety. Phase-change materials in undersuits maintain skin temperature above critical thresholds for up to 90 minutes. Hybrid drysuits with integrated flotation and quick-inflation systems address both thermal protection and buoyancy needs. Recent prototypes from Arctic research teams incorporate microclimate heating through exothermic chemical layers activated by seawater contact.Survival Case Studies: Lessons From Extreme Environments
The 2022 North Sea fishing vessel disaster demonstrated the life-saving potential of modern mitigation strategies. Crew members who completed cold water survival training achieved a 80% survival rate despite 90 minutes in 6°C water. Analysis revealed successful use of group huddling techniques and controlled breathing, maintaining core temperatures above the critical 30°C threshold. In contrast, untrained passengers succumbed to cold incapacitation within 40 minutes.Advertisement
Recommended Reading: Medication Interactions with Cold Exposure























Comments
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *